Alternative payment methods are changing the financial industry and the world.
They are improving financial inclusion, convenience, security, and innovation. Their market value is projected to reach more than $15 trillion by 2027, with a CAGR of 16.3% over the period 2017-2027.
Businesses willing to embrace them in their payment strategy will thrive in this changing economic landscape. As the philosopher Eric Hoffer wrote:
“In times of change, learners inherit the earth, while the learned find themselves beautifully equipped to deal with a world that no longer exists.”
In this blog, we explore what alternative payments are, their different types, and why businesses should be using them.
What are alternative payments?
Alternative payments (also referred to as non-traditional or emerging payment methods) are non-cash and credit or debit card-based payment options.
They can be used to shop online or in-store by consumers and businesses. They have gained popularity in recent years due to advancements in technology and changing customer preferences.
What is alternative financing?
Alternative financing refers to non-traditional methods of providing or receiving capital or funds for financial needs. Traditional financial institutions usually offer a narrow range of financing and loan products. Alternative lenders provide a more diverse set of consumer and business financing options.
The use of alternative financing might include starting a business, expanding operations, or funding specific projects. Some of them are also specific to companies working in a business-to-business (B2B) field.
They are not the same thing as alternative payments. However, they are often offered by the same payment service providers. Alternative lenders provide more financing options than lines of credit and traditional bank loans. These alternative financing options include:
- Crowdfunding (e.g., Kickstarter, Indiegogo, GoFundMe)
- Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending (e.g., LendingClub, Prosper)
- Venture capital
- Angel investing
- Invoice financing (including invoice factoring and discounting)
Different types of traditional payment methods

1. Cash
Cash is a physical currency, such as banknotes and coins. It is widely accepted for in-person transactions, although its use is rapidly declining in favor of electronic methods.
2. Checks
Checks are written orders instructing a traditional bank to pay a specified amount of money from one account to another. While check usage is declining, it is still a particularly popular B2B payment method. In fact, paper checks are still the most commonly used type of non-cash payment method in the U.S.
3. Credit cards
Credit cards, like Visa, Mastercard, and American Express, allow consumers to make purchases on credit. Cardholders repay the borrowed amount, often with interest, at a later date. Credit cards are widely accepted around the world.
4. Debit cards
Debit cards are linked to a bank account and allow users to make payments directly from their account balance. They are commonly used for both in-person and online purchases.
5. Prepaid cards and vouchers
Prepaid cards and vouchers are reloadable payment cards that consumers can use for transactions. They are not linked to a bank account or credit line, making them a useful alternative for budgeting and online transactions.
6. Bank transfers
Bank transfers involve moving money from one bank account to another, either electronically or through a bank branch. This method of bank transfer is often used for large transactions, salary deposits, and international transfers.
7. Direct debits
Direct debits allow businesses to withdraw funds directly from a customer’s bank. They are often used to pay recurring bills, such as utility bills, mortgage payments or subscriptions.
Different types of alternative payment methods
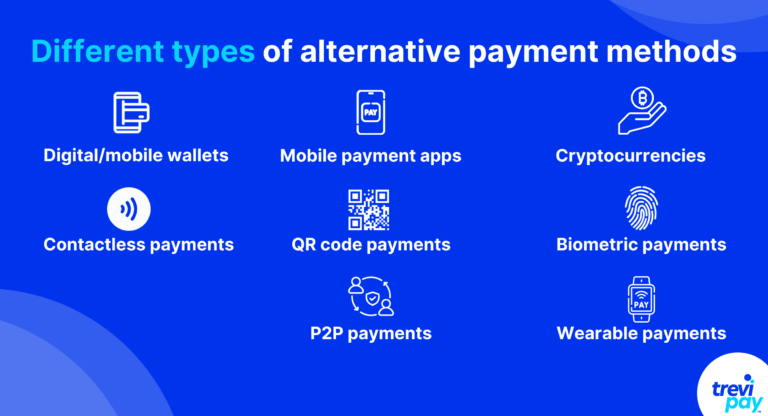
1. Digital wallets or mobile wallets
Digital wallets (also known as electronic wallets or e-wallets) allow users to store their debit or credit card, or bank account information, securely on a mobile device. They allow quick and contactless payments at physical stores, online retailers, and in-app purchases.
Examples of well-known digital wallets include, Apple Pay, Google Pay, Samsung Pay, and WeChat Pay.
2. Mobile payment apps
Mobile payment apps enable users to send money to friends and family, split bills, and make online payments using linked bank accounts or credit cards.
Popular examples include Venmo and PayPal.
3. Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies (often referred to as crypto) are decentralized digital currencies that operates on blockchain technology.
They offer a secure way to conduct transactions across borders. In recent years, they have been rapidly gaining mainstream acceptance as a form of payment by some businesses and merchants.
Famous examples of cryptocurrencies include Bitcoin, Ethereum and Litecoin.
4. Contactless payments
Contactless payments involve tapping or waving a card or mobile device near a payment terminal equipped with near-field communication (NFC) technology. This approach reduces physical contact during transactions and enhances speed and security.
5. QR code payments
QR code-based payments involve scanning a QR code displayed at a merchant’s point of sale (POS) using a mobile app. This method is prevalent in China, where Alipay and WeChat Pay are the most popular payment method methods.
6. Biometric payments
Biometric-based payment methods rely on the unique physical characteristics of users to authenticate transactions. They match users’ input with their previously stored information.
Biometrics such as fingerprint or facial recognition are increasingly being used to make secure and convenient payments.
7. Peer-to-peer (P2P) payments
P2P payments are payments made using platforms that enable individuals to send money directly to one another using email addresses or mobile phone numbers.
Well-known examples of P2P platforms include Zelle and Wise (previously TransferWise).
8. Wearable payments
Wearable payments refers to payments made using technology built into wearable devices, such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, jewelry, bags, etc. They enable users to make payments by simply tapping their wearable devices on compatible terminals.
Advantages of alternative payments
Customer convenience
The more local payment options and global payment methods businesses offer, the wider their potential customer base. And popular alternative payment methods often offer a more convenient and efficient way to make transactions than traditional methods like cash or checks.
Competitive advantage
Embracing alternative payments can set businesses apart from competitors that still relying solely on traditional payment methods. This may satisfy some clients today and send a signal to existing and potential customers about a business’ future plans.
Global reach
Some alternative payment methods can facilitate international transactions, allowing businesses to tap into a target market abroad. This is especially valuable for eCommerce companies looking to expand their customer base.
Reduced cash handling
Accepting digital payments reduces the need for handling physical cash, which can be costly and pose security risks. And it streamlines accounting and reduces the risk of errors.
Faster transactions
Many alternative payment methods, such as contactless and mobile payments, are quicker than traditional methods like cash or checks. This can lead to shorter waiting times at checkout and quicker processing.
Enhanced security
Digital payment methods often come with robust security features, including encryption, tokenization, and biometric authentication. These can reduce the risk of fraud for both businesses and customers.
Data insights
By accepting alternative payment methods, businesses can generate more transaction data. This can provide insight into customer behavior, preferences, and purchasing habits, allowing for more targeted marketing and product offerings.
Many also provide a clear transaction history. This makes it easier for users to track their spending and for businesses to maintain accurate financial records.
Improved cash flow
For businesses that offer buy-now-pay-later (BNPL) options or receive payments through digital invoices, alternative payment methods can help improve cash flow by ensuring faster payment receipt.
Environmental impact
Transitioning away from paper-based payments, such as checks, can have a positive environmental impact. It reduces paper usage and the carbon footprints.
Reduced costs
Depending on the method used, alternative payment methods can be cost-effective for businesses, potentially leading to lower transaction fees.
Disadvantages of alternative payments
Dependency on technology
Alternative payments rely heavily on technology. This means that resources are needed for setup and maintenance, and issues with it or outages can disrupt transactions.
Transaction fees
Depending on the specific payment method and the provider, there may be transaction fees or processing charges associated with alternative payments. These can affect both consumers and businesses.
Regulatory challenges
Some alternative payment methods, especially those related to cryptocurrencies, may face regulatory challenges and uncertainty in different regions.
TreviPay’s B2B payments solutions
At TreviPay, we provide a business-to-business (B2B) payment platform that helps businesses process multiple different payment methods.
It offers invoicing options at checkout, providing real-time authorization across all sales channels. It simplifies invoicing to meet buyer requirements, which reduces disputes through integrated purchase controls and improves customer experience.
It also also allows B2B businesses to offer trade credit and net terms. This enhances customer spend and loyalty, and with straightforward APIs, is easy to integrate with eCommerce platforms, accounting software, or payment gateways.
Conclusion
Alternative payment methods are steadily growing into a successful feature on the financial landscape.
Traditional payment structures, from cash and credit cards to checks and direct debits, have offered reliable, albeit sometimes cumbersome, payment methods.
With the rise of technology, accepting alternative payment methods has become easier to do. These methods range from digital wallets and cryptocurrencies to QR code and biometric payments.
These approaches offer enhanced customer satisfaction, convenience, security, and often, global applicability. But they are not without challenges – including, transaction fees, technological dependencies, and complex regulatory requirements.
Businesses must maintain a balance between the familiar reliability of traditional methods and the innovative potential offered by alternative payments.
As financial transactions become more digital and global, each alternative payment method attempts to shift towards more user-friendly transactions.
From digital wallets to cryptocurrencies and contactless payments, businesses are embracing the age-old notion that adaptability brings great rewards.