Innovation in fintech and lending solutions is making business-to-business (B2B) financing flourish.
There has never been more choice for B2B companies looking to receive or provide these services.
Businesses now need to ask which option best suits me and my clients?
In this article, we will examine the different B2B financing options available and how they work.
What is B2B financing?
B2B financing refers to financing available to businesses that work primarily with other businesses. It covers traditional bank loans and a variety of different funding and credit tools provided by alternative lenders.

Tech innovation and regulatory policies such as open banking has brought new financial players to both the business-to-consumer (B2C) and B2B worlds.
In turn, they can now enable non-financial businesses to directly provide their clients financial services via embedded financing (see below).
B2B financing has many different features to its B2C equivalent. These include, for example, the higher value of finance required and use of invoice financing.
The need for financing also arises for different reasons reasons. In B2C, it is often about wanting something sooner. In B2B, the following are usually drivers of decisions:
- Payroll funding
- Technology investment
- Inventory
- Insurance
- Managing cashflow
Each of these methods can have a positive impact on B2B eCommerce.
Traditional banks vs alternative lenders
Banks still provide the majority of financing for business, but alternative lenders’ share of the market is growing rapidly: back in 2020, despite Covid, the global online alternative finance market grew by 24% to USD $113 billion.
Some of the financing options for businesses outlined below are available from both banks and alternative lenders.
Benefits of B2B financing from alternative lenders
Each financing solution for B2B comes with its own unique advantages. Generally, there are three main benefits of using alternative lenders instead of banks.
Access
Business loan applications with banks often require a lot of supporting information and lengthy processes. There are strict regulations to comply with.
By contrast, new alternative B2B financial providers often have simpler processes and higher approval rates than traditional banks.
Back in January 2022, big banks approved 14.5% of loans and small banks 20.3%, whereas for alternative lenders that figure was 26.3%.
Speed
Alternative lenders also approve lending much quicker than banks. This is because they rely on different processes to banks to confirm funding decisions.
For example, TreviPay offers decisions on credit lines of up to USD $250,000 made by automated processes in just 30 seconds.

Flexibility
The global fintech market is predicted to enjoy a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 26.87% in the period leading up to 2026. This growth is driven by innovation.
It is also a highly competitive market. And competition benefits customers the most. Flexible payment terms, quick onboarding processes, and updates to existing technology are fast becoming the norm.
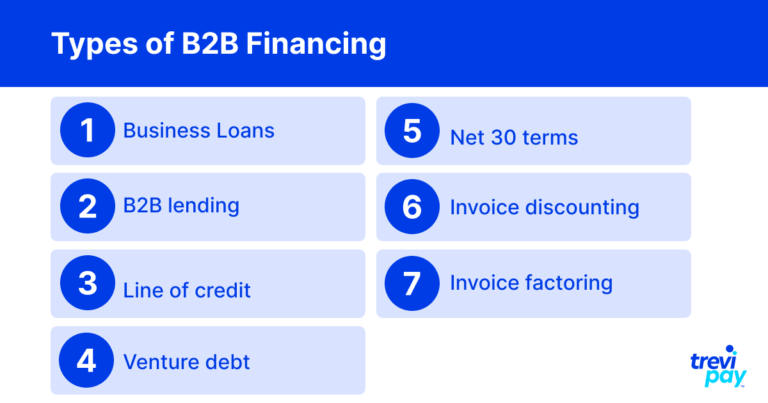
Types of B2B financing
Below is a list of the main types of financing available to companies working in the B2B space.
Business loans
Business loans are particularly useful to SMEs in the early or expansion stages of development.
To secure a business loan, companies often have to meet specific requirements set by the provider, such as creditworthiness, turnover, age of company, etc.
These requirements are generally more numerous and stringent with banks than they are with alternative lenders.
Different providers specialise in different types of loans. The types available might vary according to company size (SMEs, startups, larger corporates, etc.) and lending timeframes.
An important consideration for business loans is whether they are seen as good debt (used to boost growth and add value) or bad debt (used to prop up a failing business). Lenders are understandably keen to differentiate between the two.
B2B lending
B2B lending from alternative providers has come a long way in recent years. From simply digitalising the process (therefore making it much more accessible) to more complex solutions that also utilise online data rather than traditional asset underwriting of metrics.
Many nonbank lenders offer value-added services. These include less immediately visible benefits such as experience and advice gained from working with similar clients and networks.
Well-known B2B lending companies include C2FO, Fundera, Kabbage and Funding Circle.
Line of credit
A line of credit, sometimes called ‘revolving credit facilities’, is when a business (usually a small business) has a pre-determined credit line available with a third-party provider.
Unlike a business loan, this amount is not a sum paid upfront, but is available when needed. Besides paying back what has been borrowed, interest at a pre-agreed rate is due. It’s almost like a credit card for a business.
The primary benefit a line of credit has over a business loan is its flexibility. This is particularly suitable for businesses who are uncertain what costs they may or may not need covered.
Venture debt
Venture debt is a type of debt financing where lenders rely on the borrower’s most recent venture capital equity round as a measure for the terms provided. It is specifically aimed at young companies and startups with high growth.
The figures for this latest round of venture capital equity, reasons for the loan, and level of growth all determine the size of the venture debt.
Net 30 terms
Net terms, also known as ‘credit terms‘ or ‘trade credit‘, are essentially a delayed or grace period from when companies need to pay for goods or services.
Net terms are usually given over 30, 60 or 90-day periods – known as net-30, net-60, or net-90, respectively. Their availability is often assumed as a given in B2B transactions.
Invoice discounting
Invoice discounting is when a company borrows most of the value of their unpaid invoices from a third party. They essentially function as business loans with invoices as security.
The main benefit of invoice discounting is that it is a straightforward way to quickly boost cashflow. Clients paying the invoices usually won’t be aware of this arrangement, so from their point of view it is totally seamless.
Invoice factoring
Invoice factoring also uses invoices to secure cashflow. It does this by effectively utilising invoices as collateral which the invoice factoring provider (the factor) covers most of as soon as the invoice is issued.
It is similar to invoice discounting except the factor is paid directly by the client. The client is aware of this.
The factor also provides other services, such as collections and detailed monitoring of which items of an invoice have been paid. The benefit of this is that is saves the company using the service time and resources.
Embedded B2B financing: Offering financial services to your clients
The concepts of embedded payments and finance are essential to modern business. Used to B2C levels of seamless payments and even credit, customers in the business world increasingly expect a frictionless purchase experience.
Embedded payments
Embedded payments are payments integrated into your existing processes.
The more embedded the payments, the less friction is felt as part of the user experience. This in turn increases the likelihood of immediate and return purchases.
Embedded payments are similar to the concept of ‘invisible payments’ where users are not required to confirm a payment at the time of purchase. Perhaps the most well-known examples are the Uber experience or checkoutless Amazon Go stores.
Embedded finance
Embedded finance has been defined as “the use of financial tools or services — such as lending or payment processing — by a non-financial provider.”
By directly offering finance, B2B service providers remove another obstacle for customers, who don’t need to spend time searching and signing up with third parties.
Being able to offer financing solutions to B2B clients ensures robust cashflow, which ultimately supports sales for all parties and positive trading conditions. As with embedded payments, the more seamlessly this can be done, the better.
TreviPay offers clients the ability to offer their business customers an embedded finance solution based on a line of credit, payment by invoice and Net 30 terms.
TreviPay’s B2B financing solutions
B2B retail buyers expect efficient invoicing and payment terms for high-value, recurring purchases. But many retailers often aren’t equipped to meet these demands.
At TreviPay, we offer dedicated payment, financing, and trade credit solutions tailored for B2B retail. Our services promote customer loyalty and minimize fraud risk.
And our automated back-office tools and integrated systems streamline your operations and improve your customers’ buying experience.
Conclusion
Whether it’s via traditional or – increasingly – alternative lenders, B2B businesses can choose from multiple financing options and a range of potential service providers.
Business loans are especially popular for new companies. However, there are more innovative and flexible solutions, including lines of credit, venture debt, and invoice finance (including invoice discounting and invoice factoring).
There tends to be substantial differences between options offered by traditional banks versus alternative providers.
Banks tend to use older technology and processes. This often means slower decision-making and a more conservative attitude to risk.
Alternative or non-bank providers usually use modern technology that can evaluate applications quickly using additional datapoints. This often means faster processes and higher approval rates.
Companies can even go further and offer embedded financing solutions in the same way they offer embedded payments.
Competition caused by high growth in fintech is driving innovation in this field. Businesses looking to capitalise on this are faced with a good problem to have: too much choice.