The average invoice processing time can be between two days and two weeks.
It can require manual processing and also be quite complex with multiple fields of invoice data, authentication stages, and communications.
Using electronic invoices (e-invoices) can significantly simplify and improve this process, but it’s easy to get confused when comparing these to other forms of invoicing.
What is e-invoicing?
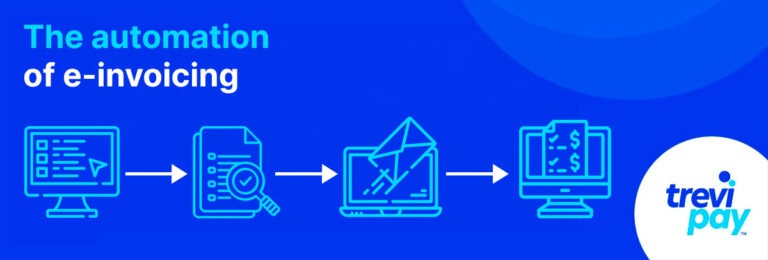
E-invoicing (also called electronic invoicing and sometimes written as eInvoicing) is a form of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) for issuing and processing invoice data in specialized and integrated electronic formats.
These formats are pre-defined. The sender and recipient’s accounting software can automatically insert and extract the data to populate relevant fields.
This electronic format is generally not readable by humans. However, versions that also provide human-readable visual formats exist. These are helpful in some circumstances.
E-invoicing is often used by companies that send a relatively high volume of invoices. Business-to-business (B2B) companies are a good example of this.
What is Electronic Data Interchange (EDI?)
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is a system for electronically exchanging data directly between computers. It is often used by businesses to send and receive documents, such as purchase orders (POs), invoices, contracts and more.
It improves the efficiency and speed with which organizations can communicate and transact with one another.
EDIs rely on set standards of data storage and presentation to ensure information is accurately extracted when sent. For example, the invoice number or date format needs to be consistent. Examples of these standards include EDIFACT, X12 and XML formats.
Is EDI always carried out online?
EDI is not always carried out online. In fact, it pre-dates the internet and early versions of it were even used as far back as the 1948 Berlin airlift.
At the time, modems based on radio and telephone technology were used for the complex military and freight logistics involved. From the 1960s onwards, similar technology was commonly used with commercial supply chain logistics, too.
e-invoices vs regular invoices
The e-invoicing process is automated whereas regular invoice processing is usually a manual process. This processing includes data entry, verification, approval, sending and more.
e-invoices vs digital invoices
Digital invoices are regular invoices, usually in pdf or word document formats. This means that they also require manual processing.
Though they are technically digital, too, e-invoices have a very specific structured form that is automatically imported and read by the buyer’s system and seller’s system.
Is e-invoicing compulsory?
Across many countries, especially those within the EU, e-invoicing is increasingly compulsory. Each country has its own requirements around it. And these requirements are subject to change.
Implementation can have an impact on companies especially when it comes to global expansion and cross-border transactions. For example, in some European countries, when e-invoice information is missing, certain sales orders simply can’t be initiated.
In others, not all businesses need to use e-invoicing, but certain suppliers must have the capabilities to accept them.
7 benefits of e-invoicing

1. Streamlines invoice processing
E-invoicing can significantly streamline the invoicing and overall order-to-cash (O2C) process.
The regular invoicing process relies on humans to initiate it. But this initiation can be delayed by a number of factors, such as weekends, holidays, spam filters or overflowing email inboxes.
2. Reduces human error
Though it varies by country, invoices typically have about 9 fields, including dates, prices, buyer information, seller information, tax codes and more.
Filling these out and manual invoice processing more broadly requires a lot of work. Automated invoicing reduces this work and does it more accurately than a human can.
3. Reduces paperwork
Paper invoices can create work. They create more manual data entry tasks. And whilst scanned paper invoices can be saved as computer files, physical copies may require physical storage space.
By removing paper from the invoice process, you can save time and space.
4. Security
XML formats and other e-invoicing standards are difficult for fraudsters to replicate.
This is useful because invoice fraud is common.
According to a report by Medius, in 2022 the average estimated cost of fraud for medium-sized businesses was over $280,000 per year. And 1 in 5 businesses saw 21 – 30 cases over the same period.
5. Data insights
E-invoicing systems can track all paid and open invoices whilst collecting, organizing and analyzing patterns and trends in spending, supplier performance and payment cycles.
This in turn helps with data analysis, which can be used to forecast cash flow and build strategic financial business intelligence.
6. Easier integration into the wide payments ecosystem
Regular paper or digital invoicing requires manual intervention to update the other systems.
But e-invoices can be integrated into other business systems that they will automatically communicate and exchange data with. These include accounting systems, ERP systems or payment orchestration systems.
This improves business processes and streamlines payment processing.
7. Reduces costs
Whether it’s by time savings, reduced fraud, less paper invoices etc., the above benefits all contribute to lower costs.
Furthermore, the knock-on effects may be hard to quantify but they are very real. Your accounts payable team can work on other tasks and strategies. They can also be better prepared for scaling up, improve vendor relationships, and generally have higher morale.
TreviPay’s invoice management solution
Our end-to-end payment and invoice management software revolutionizes B2B trading relationships. It not only offers the benefits associated with the e-invoicing process but adds other important benefits.
It enables business buyers to leverage trade credit, offers real-time authorizations across all channels, provides real-time onboarding and expands reach with invoicing and receivable management for 32 countries.
And it digitizes and automates accounts receivable processes whilst maintaining robust fraud and risk management with features like AML, KYC/KYB.
Conclusion
E-invoicing is a form of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) for issuing and processing invoices in predefined electronic formats.
It is commonly used by B2B companies that issue and process high volumes of invoices. It streamlines the payment process and reduces human error and paperwork (in both the figurative and literal sense).
It also provides robust security and valuable data insights. This helps businesses find financial patterns and make forecasts.
Unlike regular or digital invoices, e-invoices are integrated into other systems like accounting or payment orchestration systems.
E-invoicing is increasingly being required by countries which means the use of e-voicing is becoming mandatory for global expansion.
TreviPay offers automated invoicing and payment solutions to help businesses simplify international expansion and increase customer loyalty.
Explore these 7 Important B2B Payment Considerations and prepare your business for successful global expansion today.